In this lesson, we’ll explore the most frequently used tenses in English. I’ll also show you some everyday situations where you can apply these tenses.
If you like, there’s a quick quiz at the end to check your understanding.
Verb Tenses Technically, English has only three main tenses: present, past, and future. However, each tense can be divided into four different aspects: simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. When we combine these aspects with the three main tenses, we get the 12 verb tenses we commonly refer to in English.
Here’s a quick overview of each:
Present Tenses:
- Present Simple: Used for facts, habits, and permanent situations.
- Present Continuous: Describes actions happening right now or around the present moment.
- Present Perfect: Refers to past actions that have relevance to the present or experiences you’ve had.
- Present Perfect Continuous: Describes actions that started in the past and are still continuing up to the present.
Past Tenses:
- Past Simple: Used to talk about actions that were completed in the past.
- Past Continuous: Describes actions that were ongoing at a specific time in the past.
- Past Perfect: Refers to actions that were completed before a certain point in the past.
- Past Perfect Continuous: Describes actions that began in the past, continued for some time, and were finished before another past event.
Future Tenses:
- Future Simple: Used to describe actions that will take place in the future.
- Future Continuous: Refers to actions that will be ongoing at a certain point in the future.
- Future Perfect: Describes actions that will be completed before a specific moment in the future.
- Future Perfect Continuous: Used for actions that will have started at some point (past, present, or future), will continue, and will be finished before another future event.
Look at the donut chart:
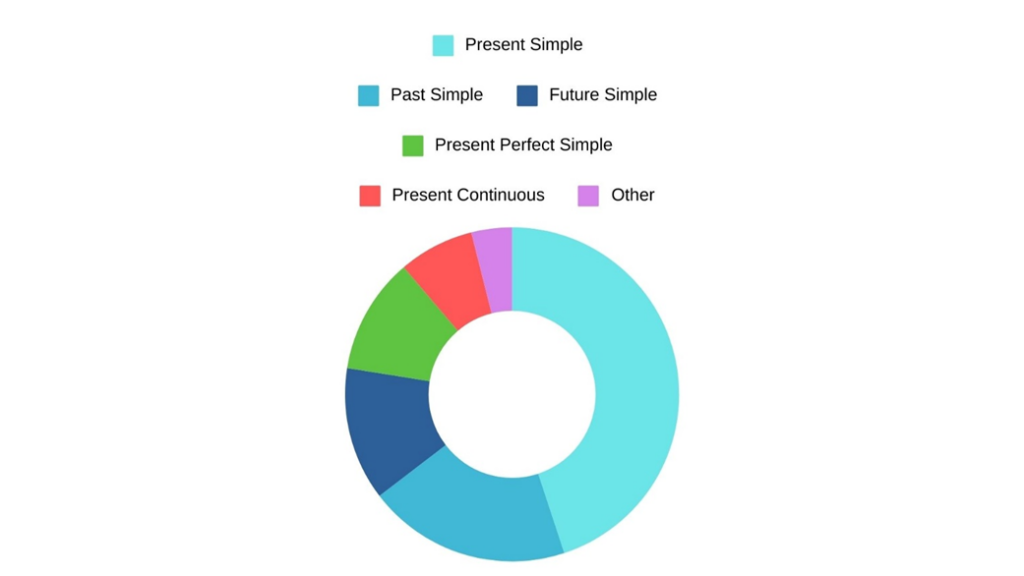
As shown in the chart above, not all verb tenses are used equally. Research reveals that the five most frequently used tenses in English are:
- Present Simple
- Past Simple
- Future Simple
- Present Perfect Simple
- Present Continuous
The small purple section on the chart represents the remaining seven verb tenses, which are used less often in day-to-day conversations.
However, don’t underestimate the other tenses. While all tenses have their place, these five are essential for everyday communication. Now, let’s explore how to use each one effectively.
Present Simple
The Present Simple is one of the most widely used tenses in English. Let’s look at its common uses:
- Facts or statements that are always true:
- Water boils at 100 °.
- Children have long Holiday in Summer.
- Statements true in the present:
- You are such a good friend, Tom!
- I can’t cook at all — look at this pasta!
- Routines or habits in the present (often with adverbs of frequency):
- Do you always drive to work?
- I never watch TV in the evening.
- Scheduled events in the future:
- My flight to Paris leaves on October 5th.
- My party kicks off at 10 p.m. Be on time!
- Directions or instructions:
- Mix the flour and water to create a thick dough.
- To get to school, walk to the corner and turn left.
As you can see, the Present Simple covers a lot of ground in daily communication.
Past Simple
The Past Simple is used often because we love to talk about the past. It’s found in news articles, books, and casual conversations. Here’s how it’s commonly used:
- Actions at a specific time in the past:
- I visited last summer with my family last Summer.
- A series of events in the past:
- Tom woke up, brushed his teeth, and headed to the office.
- Repeated or habitual actions in the past:
- Every morning, Tom met his friends at the Café for Breakfast.
- Past states or conditions:
- We were exhausted after our long hike yesterday.
Future Simple
The Future Simple allows us to talk about what will happen. It’s perfect for predictions, intentions, plans, and expectations. It’s straightforward since it uses “will” and the base form of a verb. It’s typically used for:
- Spontaneous decisions:
- I’m hungry; I’ll order some food.
- Predictions:
- The weather forecast says it will rain tomorrow.
- Promises:
- I’ll arrive at the office 20 minutes early to set everything up.
- Offers:
- Mum will help you with your project if you ask her.
- Requests:
- Will you please pass me the salt?
Present Perfect Simple
Despite its long name, the Present Perfect Simple is easy to grasp. It links the past to the present and is formed using “have” or “has” with the past participle of the main verb. It’s used for:
- Unfinished actions or states starting in the past:
- He’s been in his new role for two weeks.
- Completed actions with relevance to the present:
- My dad has just arrived at the house.
- Life experiences and events:
- They’ve traveled around Asia and most of Europe.
- Actions at an unspecified time in the past:
- Yes, we’ve tried that recipe before!
Present Continuous
We use the Present Continuous to talk about actions happening now or around the present time. It describes ongoing or temporary situations. Common uses include:
- Actions happening right now:
- Lucy is making some delicious banana pancakes.
- Temporary activities:
- I’m trying to practise yoga to see how it goes.
- Plans or future events:
- Tom isn’t attending the conference next month; he changed his mind.
- Actions happening around a specific time:
- I’m working this morning, but I’ll be free in the afternoon.
- Gradual changes or improvements:
- The city is gradually becoming more eco-friendly with new recycling programs and bike lanes.
These five tenses make up a significant portion of our everyday language. By mastering them, you’ll be able to navigate most conversations with ease!